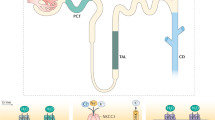
Abstract
Water excretion is regulated in large part through the regulation of osmotic water permeability of the renal collecting duct epithelium. Water permeability is controlled by vasopressin through regulation of the water channel, aquaporin-2 (AQP2). Two processes contribute: (1) regulation of AQP2 trafficking to the apical plasma membrane; and (2) regulation of the total amount of the AQP2 protein in the cells. Regulation of AQP2 abundance is defective in several water-balance disorders, including many polyuric disorders and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. Here we review vasopressin signaling in the renal collecting duct that is relevant to the two modes of water permeability regulation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH, Agre P, Knepper MA. Aquaporins in the kidney: from molecules to medicine. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:205–44.
Rojek A, Fuchtbauer EM, Kwon TH, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Severe urinary concentrating defect in renal collecting duct-selective AQP2 conditional-knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:6037–42.
Nielsen S, Smith BL, Christensen EI, Knepper MA, Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993;120:371–83.
Maeda Y, Smith BL, Agre P, Knepper MA. Quantification of aquaporin-CHIP water channel protein in microdissected renal tubules by fluorescence-based ELISA. J Clin Investig. 1995;95:422–8.
Knepper MA, Valtin H, Sands JM. Renal actions of vasopressin. In: Fray JCS, editor. Handbook of physiology: the endocrine system (section 7). New York: Oxford; 2000. p. 496–529.
Fushimi K, Uchida S, Hara Y, Hirata Y, Marumo F, Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993;361:549–52.
Ecelbarger CA, Terris J, Frindt G, Echevarria M, Marples D, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Aquaporin-3 water channel localization and regulation in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 1995;269:F663–72.
Terris J, Ecelbarger CA, Marples D, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Distribution of aquaporin-4 water channel expression within rat kidney. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 1995;269:F775–85.
Ecelbarger CA, Nielsen S, Olson BR, Murase T, Baker EA, Knepper MA, Verbalis JG. Role of renal aquaporins in escape from vasopressin-induced antidiuresis in rat. J Clin Investig. 1997;99:1852–63.
Nielsen S, Chou CL, Marples D, Christensen EI, Kishore BK, Knepper MA. Vasopressin increases water permeability of kidney collecting duct by inducing translocation of aquaporin-CD water channels to plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:1013–7.
Nielsen S, DiGiovanni SR, Christensen EI, Knepper MA, Harris HW. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of vasopressin-regulated water channel in rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:11663–7.
Hayashi M, Sasaki S, Tsuganezawa H, Monkawa T, Kitajima W, Konishi K, Fushimi K, Marumo F, Saruta T. Expression and distribution of aquaporin of collecting duct are regulated by V2 receptor in rat kidney. J Clin Investig. 1994;94:1778–83.
DiGiovanni SR, Nielsen S, Christensen EI, Knepper MA. Regulation of collecting duct water channel expression by vasopressin in Brattleboro rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:8984–8.
Hoffert JD, Chou CL, Fenton RA, Knepper MA. Calmodulin is required for vasopressin-stimulated increase in cyclic AMP production in inner medullary collecting duct. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:13624–30.
Grantham JJ, Burg MB. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966;211:255–9.
Wall SM, Han JS, Chou CL, Knepper MA. Kinetics of urea and water permeability activation by vasopressin in rat terminal IMCD. Am J Physiol. 1992;262:F989–98.
Pisitkun T, Jacob V, Schleicher SM, Chou CL, Yu MJ, Knepper MA. Akt and ERK1/2 pathways are components of the vasopressin signaling network in rat native IMCD. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2008;295:F1030–43.
Rinschen MM, Yu MJ, Wang G, Boja ES, Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals vasopressin V2-receptor-dependent signaling pathways in renal collecting duct cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:3887.
Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Saeed F, Song JH, Chou CL, Knepper MA. Dynamics of the G protein-coupled vasopressin V2 receptor signaling network revealed by quantitative phosphoproteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012;11:M111.
Nedvetsky PI, Tabor V, Tamma G, Beulshausen S, Skroblin P, Kirschner A, Mutig K, Boltzen M, Petrucci O, Vossenkamper A, Wiesner B, Bachmann S, Rosenthal W, Klussmann E. Reciprocal regulation of aquaporin-2 abundance and degradation by protein kinase A and p38-MAP kinase. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:1645–56.
Douglass J, Gunaratne R, Bradford D, Saeed F, Hoffert JD, Steinbach PJ, Knepper MA, Pisitkun T. Identifying protein kinase target preferences using mass spectrometry. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;303:C715–27.
Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Wang G, Shen RF, Knepper MA. Quantitative phosphoproteomics of vasopressin-sensitive renal cells: regulation of aquaporin-2 phosphorylation at two sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:7159–64.
Nishimoto G, Zelenina M, Li D, Yasui M, Aperia A, Nielsen S, Nairn AC. Arginine vasopressin stimulates phosphorylation of aquaporin-2 in rat renal tissue. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:F254–9.
Hoffert JD, Fenton RA, Moeller HB, Simons B, Tchapyjnikov D, McDill BW, Yu MJ, Pisitkun T, Chen F, Knepper MA. Vasopressin-stimulated increase in phosphorylation at Ser269 potentiates plasma membrane retention of aquaporin-2. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:24617–27.
Fenton RA, Moeller HB, Hoffert JD, Yu M-J, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Acute regulation of aquaporin-2 phosphorylation at Ser-264 by vasopressin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:3134–9.
Moeller HB, Knepper MA, Fenton RA. Serine 269 phosphorylated aquaporin-2 is targeted to the apical membrane of collecting duct principal cells. Kidney Int. 2008;75:295–303.
Hoffert JD, Nielsen J, Yu MJ, Pisitkun T, Schleicher SM, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Dynamics of aquaporin-2 serine-261 phosphorylation in response to short-term vasopressin treatment in collecting duct. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2007;292:F691–700.
Xie L, Hoffert JD, Chou CL, Yu MJ, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA, Fenton RA. Quantitative analysis of aquaporin-2 phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2010;298:F1018–23.
Star RA, Nonoguchi H, Balaban R, Knepper MA. Calcium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate as second messengers for vasopressin in the rat inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Investig. 1988;81:1879–88.
Chou CL, Yip KP, Knepper MA. Role of Ca/calmodulin in vasopressin-stimulated aquaporin-2 trafficking in rat collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:13A.
Yip KP. Coupling of vasopressin-induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and apical exocytosis in perfused rat kidney collecting duct. J Physiol. 2002;538:891–9.
Yip KP. Epac-mediated Ca2+ mobilization and exocytosis in inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2006;291:F882–90.
Kortenoeven ML, Trimpert C, van den BM, Li Y, Wetzels JF, Deen PM. In mpkCCD cells, long-term regulation of aquaporin-2 by vasopressin occurs independent of protein kinase A and CREB but may involve Epac. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2012;302:F1395–401.
Chou CL, Christensen BM, Frische S, Vorum H, Desai RA, Hoffert JD, de Lanerolle P, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Non-muscle myosin II and myosin light chain kinase are downstream targets for vasopressin signaling in the renal collecting duct. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:49026–35.
Chou CL, Yip KP, Michea L, Kador K, Ferraris J, Wade JB, Knepper MA. Regulation of aquaporin-2 trafficking by vasopressin in renal collecting duct: roles of ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ stores and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36839–46.
Chou CL, Yu MJ, Kassai EM, Morris RG, Hoffert JD, Wall SM, Knepper MA. Roles of basolateral solute uptake via NKCC1 and of myosin II in vasopressin-induced cell swelling in inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2008;295:F192–201.
Ando Y, Jacobson HR, Breyer MD. Phorbol ester and A23187 have additive but mechanistically separate effects on vasopressin action in rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Investig. 1988;81:1578–84.
Dixon BS, Breckon R, Burke C, Anderson RJ. Phorbol esters inhibit adenylate cyclase activity in cultured collecting tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1988;254:C183–91.
Chou CL, Rapko SI, Knepper MA. Phosphoinositide signaling in rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:F564–72.
Klussmann E, Tamma G, Lorenz D, Wiesner B, Maric K, Hofmann F, Aktories K, Valenti G, Rosenthal W. An inhibitory role of Rho in the vasopressin-mediated translocation of aquaporin-2 into cell membranes of renal principal cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20451–7.
van Balkom BW, Hoffert JD, Chou CL, Knepper MA. Proteomic analysis of long-term vasopressin action in the inner medullary collecting duct of the Brattleboro rat. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2004;286:F216–24.
Chen SY, Bhargava A, Mastroberardino L, Meijer OC, Wang J, Buse P, Firestone GL, Verrey F, Pearce D. Epithelial sodium channel regulated by aldosterone-induced protein SGK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:2514–9.
Uawithya P, Pisitkun T, Ruttenberg BE, Knepper MA. Transcriptional profiling of native inner medullary collecting duct cells from rat kidney. Physiol Genomics. 2008;32:229–53.
Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP. Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science. 2001;293:1107–12.
Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Snyder PM, Fejes-Toth G. The kidney-specific WNK1 isoform is induced by aldosterone and stimulates epithelial sodium channel-mediated Na+ transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:17434–9.
Klokkers J, Langehanenberg P, Kemper B, Kosmeier S, von Bally G, Riethmuller C, Wunder F, Sindic A, Pavenstadt H, Schlatter E, Edemir B. Atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide signaling antagonizes vasopressin-mediated water permeability in inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2009;297:F693–703.
Bouley R, Breton S, Sun T, McLaughlin M, Nsumu NN, Lin HY, Ausiello DA, Brown D. Nitric oxide and atrial natriuretic factor stimulate cGMP-dependent membrane insertion of aquaporin 2 in renal epithelial cells. J Clin Investig. 2000;106:1115–26.
Stewart GS, Thistlethwaite A, Lees H, Cooper GJ, Smith C. Vasopressin regulation of the renal UT-A3 urea transporter. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2009;296:F642–8.
Mansley MK, Wilson SM. Dysregulation of epithelial Na+ absorption induced by inhibition of the kinases TORC1 and TORC2. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;161:1778–92.
Rao R, Patel S, Hao C, Woodgett J, Harris R. GSK3beta mediates renal response to vasopressin by modulating adenylate cyclase activity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:428–37.
Torres VE, Sweeney WE Jr, Wang X, Qian Q, Harris PC, Frost P, Avner ED. EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition attenuates the development of PKD in Han:SPRD rats. Kidney Int. 2003;64:1573–9.
Breyer MD, Jacobson HR, Breyer JA. Epidermal growth factor inhibits the hydroosmotic effect of vasopressin in the isolated perfused rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Investig. 1988;82:1313–20.
Bustamante M, Hasler U, Kotova O, Chibalin AV, Mordasini D, Rousselot M, Vandewalle A, Martin PY, Feraille E. Insulin potentiates AVP-induced AQP2 expression in cultured renal collecting duct principal cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2005;288:F334–44.
Zhao B, Knepper MA, Chou CL, Pisitkun T. Large-scale phosphotyrosine proteomic profiling of rat renal collecting duct epithelium reveals predominance of proteins involved in cell polarity determination. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;302:C27–45.
Bansal AD, Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Hwang S, Chou CL, Boja ES, Wang G, Knepper MA. Phosphoproteomic profiling reveals vasopressin-regulated phosphorylation sites in collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:303–15.
Bolger SJ, Gonzales Hurtado PA, Hoffert JD, Saeed F, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA. Quantitative phosphoproteomics in nuclei of vasopressin-sensitive renal collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;303:C1006–20.
Gunaratne R, Braucht DW, Rinschen MM, Chou CL, Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals cAMP/vasopressin-dependent signaling pathways in native renal thick ascending limb cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:15653–8.
Schenk LK, Bolger SJ, Luginbuhl K, Gonzales PA, Rinschen MM, Yu MJ, Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA. Quantitative proteomics identifies vasopressin-responsive nuclear proteins in collecting duct cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1008–18.
Fang D, Hawke D, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Meisenhelder J, Nika H, Mills GB, Kobayashi R, Hunter T, Lu Z. Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by AKT promotes beta-catenin transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:11221–9.
Daugherty RL, Gottardi CJ. Phospho-regulation of beta-catenin adhesion and signaling functions. Physiology (Bethesda). 2007;22:303–9.
Pulverer BJ, Kyriakis JM, Avruch J, Nikolakaki E, Woodgett JR. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991;353:670–4.
Adler V, Polotskaya A, Wagner F, Kraft AS. Affinity-purified c-Jun amino-terminal protein kinase requires serine/threonine phosphorylation for activity. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:17001–5.
Smeal T, Binetruy B, Mercola DA, Birrer M, Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991;354:494–6.
Yu MJ, Miller RL, Uawithya P, Rinschen MM, Khositseth S, Braucht DW, Chou CL, Pisitkun T, Nelson RD, Knepper MA. Systems-level analysis of cell-specific AQP2 gene expression in renal collecting duct. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:2441–6.
Yasui M, Zelenin SM, Celsi G, Aperia A. Adenylate cyclase-coupled vasopressin receptor activates AQP2 promoter via a dual effect on CRE and AP1 elements. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 1997;272:F443–50.
Yang CX, Chen HQ, Chen C, Yu WP, Zhang WC, Peng YJ, He WQ, Wei DM, Gao X, Zhu MS. Microfilament-binding properties of N-terminal extension of the isoform of smooth muscle long myosin light chain kinase. Cell Res. 2006;16:367–76.
Ecelbarger CA, Chou CL, Lolait SJ, Knepper MA, DiGiovanni SR. Evidence for dual signaling pathways for V2 vasopressin receptor in rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:F623–33.
Ankorina-Stark I, Haxelmans S, Schlatter E. Functional evidence for the regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ activity via V1A-receptors and beta-adrenoceptors in rat CCD. Cell Calcium. 1997;21:163–71.
Tashima Y, Kohda Y, Nonoguchi H, Ikebe M, Machida K, Star RA, Tomita K. Intranephron localization and regulation of the V1a vasopressin receptor during chronic metabolic acidosis and dehydration in rats. Pflugers Arch. 2001;442:652–61.
Carmosino M, Brooks HL, Cai Q, Davis LS, Opalenik S, Hao C, Breyer MD. Axial heterogeneity of vasopressin-receptor subtypes along the human and mouse collecting duct. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2007;292:F351–60.
Izumi Y, Hori K, Nakayama Y, Kimura M, Hasuike Y, Nanami M, Kohda Y, Otaki Y, Kuragano T, Obinata M, Kawahara K, Tanoue A, Tomita K, Nakanishi T, Nonoguchi H. Aldosterone requires vasopressin V1a receptors on intercalated cells to mediate acid-base homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:673–80.
Barile M, Pisitkun T, Yu MJ, Chou CL, Verbalis MJ, Shen RF, Knepper MA. Large scale protein identification in intracellular aquaporin-2 vesicles from renal inner medullary collecting duct. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005;4:1095–106.
Nedvetsky PI, Stefan E, Frische S, Santamaria K, Wiesner B, Valenti G, Hammer JA III, Nielsen S, Goldenring JR, Rosenthal W, Klussmann E. A role of myosin Vb and Rab11-FIP2 in the aquaporin-2 shuttle. Traffic. 2007;8:110–23.
Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Kinetic model of water and urea permeability regulation by vasopressin in collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:F214–24.
Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Vasopressin activates collecting duct urea transporters and water channels by distinct physical processes. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:F204–13.
Brown D. The ins and outs of aquaporin-2 trafficking. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2003;284:F893–901.
Brown D, Hasler U, Nunes P, Bouley R, Lu HA. Phosphorylation events and the modulation of aquaporin 2 cell surface expression. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008;17:491–8.
Lu H, Sun TX, Bouley R, Blackburn K, McLaughlin M, Brown D. Inhibition of endocytosis causes phosphorylation (S256)-independent plasma membrane accumulation of AQP2. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2004;286:F233–43.
Simon H, Gao Y, Franki N, Hays RM. Vasopressin depolymerizes apical F-actin in rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:C757–62.
Valenti G, Procino G, Tamma G, Carmosino M, Svelto M. Minireview: aquaporin 2 trafficking. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5063–70.
Lang P, Gesbert F, Delespine-Carmagnat M, Stancou R, Pouchelet M, Bertoglio J. Protein kinase A phosphorylation of RhoA mediates the morphological and functional effects of cyclic AMP in cytotoxic lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1996;15:510–9.
Tamma G, Klussmann E, Procino G, Svelto M, Rosenthal W, Valenti G. cAMP-induced AQP2 translocation is associated with RhoA inhibition through RhoA phosphorylation and interaction with RhoGDI. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:1519–25.
Tamma G, Klussmann E, Maric K, Aktories K, Svelto M, Rosenthal W, Valenti G. Rho inhibits cAMP-induced translocation of aquaporin-2 into the apical membrane of renal cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2001;281:F1092–101.
Noda Y, Horikawa S, Katayama Y, Sasaki S. Water channel aquaporin-2 directly binds to actin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322:740–5.
Noda Y, Horikawa S, Katayama Y, Sasaki S. Identification of a multiprotein “motor” complex binding to water channel aquaporin-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330:1041–7.
Noda Y, Horikawa S, Kanda E, Yamashita M, Meng H, Eto K, Li Y, Kuwahara M, Hirai K, Pack C, Kinjo M, Okabe S, Sasaki S. Reciprocal interaction with G-actin and tropomyosin is essential for aquaporin-2 trafficking. J Cell Biol. 2008;182:587–601.
Tamma G, Klussmann E, Oehlke J, Krause E, Rosenthal W, Svelto M, Valenti G. Actin remodeling requires ERM function to facilitate AQP2 apical targeting. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:3623–30.
Hoffert JD, Wang G, Pisitkun T, Shen RF, Knepper MA. An automated platform for analysis of phosphoproteomic datasets: application to kidney collecting duct phosphoproteins. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:3501–8.
Tamma G, Robben JH, Trimpert C, Boone M, Deen PM. Regulation of AQP2 localization by S256 and S261 phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;300:C636–46.
Boone M, Kortenoeven ML, Robben JH, Tamma G, Deen PM. Counteracting vasopressin-mediated water reabsorption by ATP, dopamine, and phorbol esters: mechanisms of action. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2011;300:F761–71.
Lu HJ, Matsuzaki T, Bouley R, Hasler U, Qin QH, Brown D. The phosphorylation state of serine 256 is dominant over that of serine 261 in the regulation of AQP2 trafficking in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2008;295:F290–4.
Moeller HB, Praetorius J, Rutzler MR, Fenton RA. Phosphorylation of aquaporin-2 regulates its endocytosis and protein-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:424–9.
Rice WL, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Matsuzaki T, Brown D, Lu HA. Differential, phosphorylation dependent trafficking of AQP2 in LLC-PK1 cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e32843.
Kanno K, Sasaki S, Hirata Y, Ishikawa S, Fushimi K, Nakanishi S, Bichet DG, Marumo F. Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 in patients with diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1540–5.
Pisitkun T, Shen RF, Knepper MA. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:13368–73.
Pisitkun T, Johnstone R, Knepper MA. Discovery of urinary biomarkers. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1760–71.
Gonzales PA, Pisitkun T, Hoffert JD, Tchapyjnikov D, Star RA, Kleta R, Wang NS, Knepper MA. Large-scale proteomics and phosphoproteomics of urinary exosomes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:363–79.
Elliot S, Goldsmith P, Knepper M, Haughey M, Olson B. Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 in humans: a potential marker of collecting duct responsiveness to vasopressin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7:403–9.
Deen PM, van Aubel RA, van Lieburg AF, van Os CH. Urinary content of aquaporin 1 and 2 in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7:836–41.
Saito T, Ishikawa SE, Sasaki S, Nakamura T, Rokkaku K, Kawakami A, Honda K, Marumo F, Saito T. Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 in the diagnosis of central diabetes insipidus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:1823–7.
Rai T, Sekine K, Kanno K, Hata K, Miura M, Mizushima A, Marumo F, Sasaki S. Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 water channel protein in human and rat. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:1357–62.
Fernandez-Llama P, Turner R, DiBona G, Knepper M. Renal expression of aquaporins in liver cirrhosis induced by chronic bile duct ligation in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:1950–7.
Gonzales P, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA. Urinary exosomes: is there a future? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:1799–801.
van Balkom BW, Pisitkun T, Verhaar MC, Knepper MA. Exosomes and the kidney: prospects for diagnosis and therapy of renal diseases. Kidney Int. 2011;80:1138–45.
Tamarappoo BK, Verkman AS. Defective aquaporin-2 trafficking in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and correction by chemical chaperones. J Clin Investig. 1998;101:2257–67.
Kamsteeg EJ, Hendriks G, Boone M, Konings IB, Oorschot V, van der SP, Klumperman J, Deen PM. Short-chain ubiquitination mediates the regulated endocytosis of the aquaporin-2 water channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:18344–9.
Sandoval P, Slentz D, Pisitkun T, Yu M-J, Miller RL, Hoffert J, Knepper MA. LC–MS/MS-based large-scale profiling of protein half lives in renal collecting duct cells reveals that vasopressin increases half-life of aquaporin-2 protein. FASEB J. 2011;25:1039.37.
Terris J, Ecelbarger CA, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Long-term regulation of four renal aquaporins in rat. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:F414–22.
Kitamura M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the kidney. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008;12:317–25.
Hayashi M, Sasaki S, Tsuganezawa H, Monkawa T, Kitajima W, Konishi K, Fushimi K, Marumo F, Saruta T. Role of vasopressin V2 receptor in acute regulation of aquaporin-2. Kidney Blood Press Res. 1996;19:32–7.
Parker R, Sheth U. P bodies and the control of mRNA translation and degradation. Mol Cell. 2007;25:635–46.
Liu J. Control of protein synthesis and mRNA degradation by microRNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:214–21.
Bens M, Vallet V, Cluzeaud F, Pascual-Letallec L, Kahn A, Rafestin-Oblin ME, Rossier BC, Vandewalle A. Corticosteroid-dependent sodium transport in a novel immortalized mouse collecting duct principal cell line. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:923–34.
Hasler U, Mordasini D, Bens M, Bianchi M, Cluzeaud F, Rousselot M, Vandewalle A, Feraille E, Martin PY. Long term regulation of aquaporin-2 expression in vasopressin-responsive renal collecting duct principal cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:10379–86.
Saito T, Ishikawa S, Sasaki S, Higashiyama M, Nagasaka S, Fujita N, Fushimi K, Marumo F. Lack of vasopressin-independent upregulation of AQP-2 gene expression in homozygous Brattleboro rats. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:R427–33.
Uchida S, Sasaki S, Fushimi K, Marumo F. Isolation of human aquaporin-CD gene. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:23451–5.
Tchapyjnikov D, Li Y, Pisitkun T, Hoffert JD, Yu MJ, Knepper MA. Proteomic profiling of nuclei from native renal inner medullary collecting duct cells using LC–MS/MS. Physiol Genomics. 2010;40:167–83.
Rai T, Uchida S, Marumo F, Sasaki S. Cloning of rat and mouse aquaporin-2 gene promoters and identification of a negative cis-regulatory element. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:F264–73.
Nielsen J, Hoffert JD, Knepper MA, Agre P, Nielsen S, Fenton RA. Proteomic analysis of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: mechanisms for aquaporin 2 down-regulation and cellular proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:3634–9.
Hozawa S, Holtzman EJ, Ausiello DA. cAMP motifs regulating transcription in the aquaporin-2 gene. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:C1695–702.
Matsumura Y, Uchida S, Rai T, Sasaki S, Marumo F. Transcriptional regulation of aquaporin-2 water channel gene by cAMP. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:861–7.
Furuno M, Uchida S, Marumo F, Sasaki S. Repressive regulation of the aquaporin-2 gene. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:F854–60.
Uchida S, Matsumura Y, Rai T, Sasaki S, Marumo F. Regulation of aquaporin-2 gene transcription by GATA-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;232:65–8.
Hasler U, Jeon US, Kim JA, Mordasini D, Kwon HM, Feraille E, Martin PY. Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein is an essential regulator of aquaporin-2 expression in renal collecting duct principal cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1521–31.
Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J, Rao A. Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev. 2003;17:2205–32.
Li SZ, McDill BW, Kovach PA, Ding L, Go WY, Ho SN, Chen F. Calcineurin-NFATc signaling pathway regulates AQP2 expression in response to calcium signals and osmotic stress. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C1606–16.
Cha JH, Woo SK, Han KH, Kim YH, Handler JS, Kim J, Kwon HM. Hydration status affects nuclear distribution of transcription factor tonicity responsive enhancer binding protein in rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:2221–30.
Schmale H, Richter D. Single base deletion in the vasopressin gene is the cause of diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro rats. Nature. 1984;308:705–9.
Kishore BK, Terris JM, Knepper MA. Quantitation of aquaporin-2 abundance in microdissected collecting ducts: axial distribution and control by AVP. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:F62–70.
Cadnapaphornchai MA, Summer SN, Falk S, Thurman JM, Knepper MA, Schrier RW. Effect of primary polydipsia on aquaporin and sodium transporter abundance 1. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2003;285:F965–71.
Valtin H. “Drink at least eight glasses of water a day.” Really? Is there scientific evidence for “8 × 8”? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2002;283:R993–1004.
Harbaugh C, Knepper MA. Do you have a drinking problem? Run Times. 2007;9:14–7.
Bichet DG. Hereditary polyuric disorders: new concepts and differential diagnosis 6. Semin Nephrol. 2006;26:224–33.
Deen PM, Marr N, Kamsteeg EJ, van Balkom BW. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2000;9:591–5.
Frokiaer J, Marples D, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Bilateral ureteral obstruction downregulates expression of vasopressin-sensitive AQP-2 water channel in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:F657–68.
Frokiaer J, Christensen BM, Marples D, Djurhuus JC, Jensen UB, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Downregulation of aquaporin-2 parallels changes in renal water excretion in unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:F213–23.
Li C, Wang W, Kwon TH, Isikay L, Wen JG, Marples D, Djurhuus JC, Stockwell A, Knepper MA, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J. Downregulation of AQP1, -2, and -3 after ureteral obstruction is associated with a long-term urine-concentrating defect. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2001;281:F163–71.
Marples D, Frokiaer J, Dorup J, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Hypokalemia-induced downregulation of aquaporin-2 water channel expression in rat kidney medulla and cortex. J Clin Investig. 1996;97:1960–8.
Amlal H, Krane CM, Chen Q, Soleimani M. Early polyuria and urinary concentrating defect in potassium deprivation. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2000;279:F655–63.
Earm JH, Christensen BM, Frokiaer J, Marples D, Han JS, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Decreased aquaporin-2 expression and apical plasma membrane delivery in kidney collecting ducts of polyuric hypercalcemic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:2181–93.
Marples D, Christensen S, Christensen EI, Nielsen S. Lithium-induced downregulation of aquaporin-2 water channel expression in rat kidney medulla. J Clin Investig. 1995;95:1838–45.
Christensen S, Kusano E, Yusufi AN, Murayama N, Dousa TP. Pathogenesis of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus due to chronic administration of lithium in rats. J Clin Investig. 1985;75:1869–79.
Laursen UH, Pihakaski-Maunsbach K, Kwon TH, Ostergaard JE, Nielsen S, Maunsbach AB. Changes of rat kidney AQP2 and Na, K-ATPase mRNA expression in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2004;97:e1–16.
Li Y, Shaw S, Kamsteeg EJ, Vandewalle A, Deen PM. Development of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is dissociated from adenylyl cyclase activity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1063–72.
Schrier RW, Ohara M, Rogachev B, Xu L, Knotek M. Aquaporin-2 water channels and vasopressin antagonists in edematous disorders. Mol Genet Metab. 1998;65:255–63.
Nielsen S, Terris J, Andersen D, Ecelbarger C, Frokiaer J, Jonassen T, Marples D, Knepper MA, Petersen JS. Congestive heart failure in rats is associated with increased expression and targeting of aquaporin-2 water channel in collecting duct. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:5450–5.
Xu DL, Martin PY, Ohara M, St JJ, Pattison T, Meng X, Morris K, Kim JK, Schrier RW. Upregulation of aquaporin-2 water channel expression in chronic heart failure rat. J Clin Investig. 1997;99:1500–5.
Veeraveedu PT, Watanabe K, Ma M, Palaniyandi SS, Yamaguchi K, Suzuki K, Kodama M, Aizawa Y. Effects of nonpeptide vasopressin V2 antagonist tolvaptan in rats with heart failure. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;74:1466–75.
Robertson GL. Vaptans for the treatment of hyponatremia. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7:151–61.
Jonassen TEN, Nielsen S, Christensen S, Petersen JS. Decreased vasopressin-mediated renal water reabsorption in rats with compensated liver cirrhosis. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:F216–25.
Fujita N, Ishikawa SE, Sasaki S, Fujisawa G, Fushimi K, Marumo F, Saito T. Role of water channel AQP-CD in water retention in SIADH and cirrhotic rats. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:F926–31.
Fernandez-Llama P, Jimenez W, Bosch-Marce M, Arroyo V, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Dysregulation of renal aquaporins and Na–Cl cotransporter in CCl4-induced cirrhosis. Kidney Int. 2000;58:216–28.
Apostol E, Ecelbarger CA, Terris T, Bradford AD, Andrews P, Knepper MA. Reduced renal medullary water channel expression in puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:15–24.
Fernandez-Llama P, Andrews P, Ecelbarger CA, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Concentrating defect in experimental nephrotic syndrome: altered expression of aquaporins and thick ascending limb Na+ transporters. Kidney Int. 1998;54:170–9.
Saito T, Higashiyama M, Nagasaka S, Sasaki S, Saito T, Ishikawa SE. Role of aquaporin-2 gene expression in hyponatremic rats with chronic vasopressin-induced antidiuresis. Kidney Int. 2001;60:1266–76.
Ecelbarger CA, Chou CL, Lee AJ, DiGiovanni SR, Verbalis JG, Knepper MA. Escape from vasopressin-induced antidiuresis: role of vasopressin resistance of the collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:F1161–6.
Levtchenko EN, Monnens LA. Nephrogenic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:2839–43.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, J.L.L., Miranda, C.A. & Knepper, M.A. Vasopressin and the regulation of aquaporin-2. Clin Exp Nephrol 17, 751–764 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-013-0789-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-013-0789-5